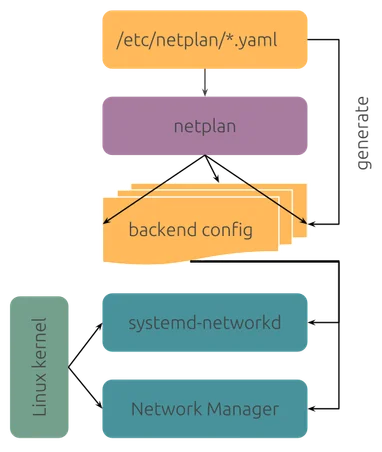
Arquitectura para un CMS Gratuito en Cloudflare (Estilo WordPress)
¿Te imaginas tener tu propio CMS (sistema de gestión de contenidos) parecido a WordPress, pero sin tener que pagar absolutamente nada por alojamiento web mensual, y además con una velocidad...











![Illuminate \ Database \ QueryException PHP SQLSTATE[HY000] [2002] No such file or directory select * from sessions where id = B9e limit 1](/images/uploads/2025/01/image-2_thumb.webp)